Loops¶
What are they?¶
Loops in any programming languages are the foundations when we are working with arrays, lists, and the elements stored inside them. A traditional loop will always have a starting point and an ending point. Loops are handy because they save time, reduce errors, and they make code more readable.
For loops¶
For loops are commonly used when we want to loop through an array and access the elements within them; this works with any collection interface that inherits the iterable interface.
Kotlin For Loop
Explanation: Inside our sample program, we declared an immutable list of strings and stored four colors within it. We declared our for loop with the syntax: for(x in ...). This means that for every x that is inside our list, we will perform the action of printing x. x represents the elements within our list, and it will continue to move on to the next element as our loop continues. For example, the first time the loop executes, x will be "Red"; the second time, it will be "Blue"; and it will stop when it reaches "Yellow", which is the last element within the list.
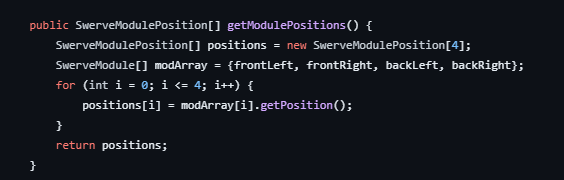
For Loops in Robotics: For loops are quite common in robotics programming because arrays and lists store information, and loops are necessary to access individual elements in a precise and understandable manner.
For example:
Explanation: Don't let all of that Java code confuse you! All we will be taking a look at is a SwerveModulePosition array called positions that will be holding the positions of the four swerve modules. In the traditional for loop, we will start at 0 and end at 4. The operation is that we will be storing the position information into our newly created SwerveModulePosition array. This is a fantastic example of a for loop in action because it shows us how accessing and storing information can be done within a few lines of code.
Here are some more examples with for loops!:
Range Expression inside For Loops
"withIndex" in For Loops
Explanation: There are a lot of things that we can add into a for loop, just like the withIndex keyword. This way of manipulating a for loop allows us to not only have access to the value, but also access to the index of the current element that we are looping through.
While Loops¶
While loops are very similar to for loops in the way that they all loop through a collection. A for loop will stop once it reaches the end of the collection; However, a while loop will continue as long as a specified condition is reached.
Kotlin While Loop
Explanation: In this example code fragment, we initialized a mutable integer variable i to the value 0. In our while loop condition, we established that the loop will continue to run as long as the value of i is less than 5; if it is, we will print out the current value of i and increment i by 1.